

After immediate extraction the wound healed without further coplications. There was only one case of dehiscence of the wound and irritation by migrated K-wire. The evaluation of results of the surgical treatment shows that in all cases clinical asymptomatic healing was achieved in 3 to 6 months (on average 4 months). For fixation they use a simple but stable tension wire loop without further fixation by plaster cast. The operation consists in decortication, local wide resection of non-union, excochleation of residual fibrous mass and implantation of autologous cortico-cancellous bone graft and with cancellous bone onlaygraft.
#Jones fracture full#
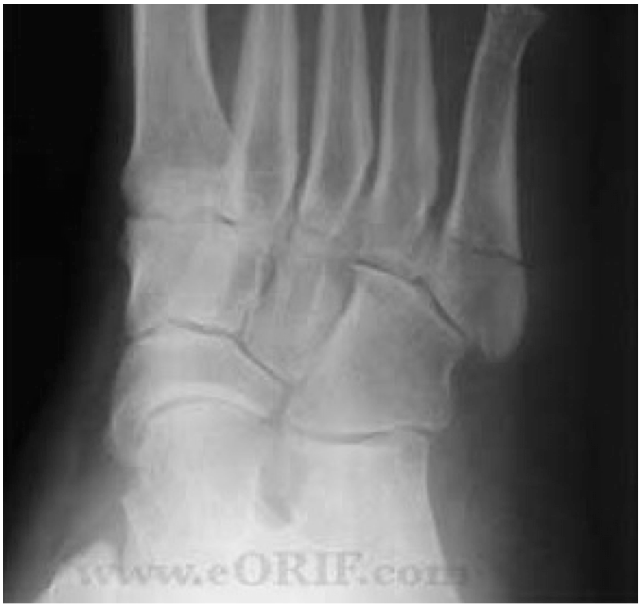
They should be made with the foot in full flexion.4.
These need to be taken from anteroposterior, oblique, and lateral views.
In case of clinically and radiographically evident non-union with the nature of fatigue fracture they indicate surgical treatment in all cases. DiagnosisA patient with a Jones fracture may not realize that it is a fracture, and could mistake it for a sprain.
The diagnosis is made with general diagnostic x-rays.
#Jones fracture professional#
As a result they recommend in case of physically active patients and professional sportsmen to choose surgical treatment. In delayed healing or re-fractures it was often necessary to prolong the cast plaster immobilization. In case the period of fixation without weight-bearing was observed the authors recorded in their study no nonunion necessitating a surgical treatment. In the first case of acute fracture non-walking plaster cast for the period of 6 to 8 weeks is recommended. The latter group the authors subdivide (not only with regard to the method of treatment) after Torg et al (1984) into acute type of Jones fracture, delayed healing or refracture in chronic complaints of patients and the actual typical stress fracture with a developed non-union. While the fractures of diaphysis may be successfully treated using walking plaster cast for 4 to 6 weeks and in case of auvulsion fractures of the base for 3 to 5 weeks (they may be treated also without rigid fixation), the treatment of metadiaphyseal fractures still poses a problem. the actual Jones fractures - and intra-articular avulsion fractures of the base. From the anatomical and biomechanical viewpoints they classify the fractures into fractures of diaphysis, extra-articular fractures of proximal metadiaphysis - i.e. The authors deal with the issues of traumatology of proximal part of 5th metatarsus and evaluate their experience in the treatment of a specific type of fracture in this region, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
